`
|
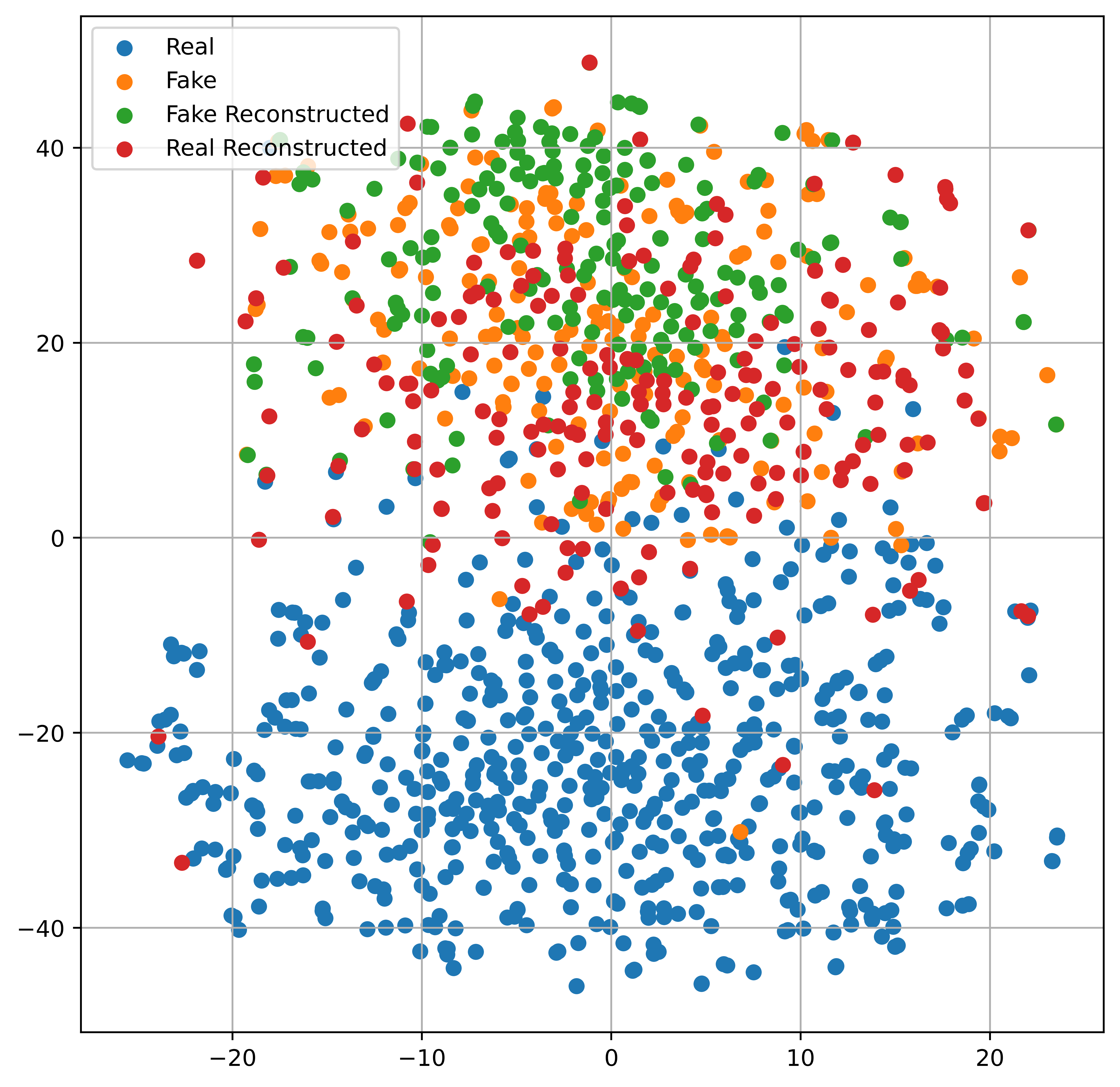
Perceptual Classifiers: Detecting Generative Images using Perceptual Features
-
We believe that effectively modeling the distribution of real images can help improve the generalization abilities of classifiers in detecting fake images.
-
We conduct extensive experiments to validate the performance of classifiers trained on feature space of IQA models, on multiple datasets and study their generalization capabilities on images synthesized by unseen generative models including multiple variants of Stable Diffusion, Latent Diffusion models, Midjourney and Auto-Regressive models.
-
We demonstrate that perceptual classifiers achieve state-of-the-art performance on multiple datasets and exhibit good robustness to various image degradations without requiring pre-training on internet-scale datasets.
-
Submitted to ICIP 2025.
|

|
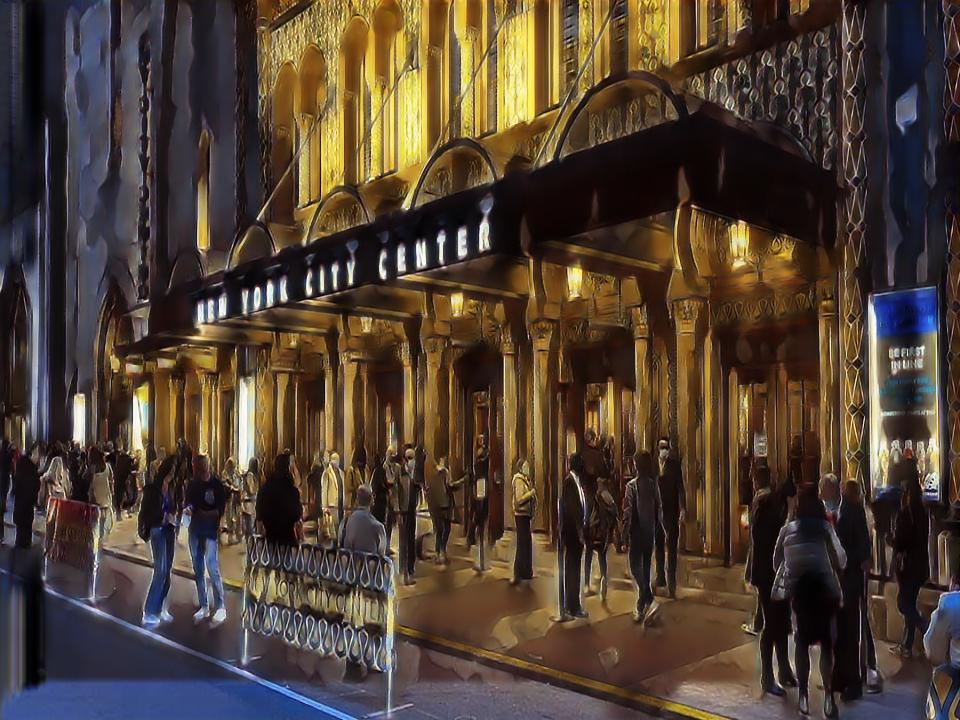
Impact of Backbone Models and Dataset on Cartoonization Performance
-
Explored the impact of backbone architecture namely VGG19 and ViT-B/16 in the cartoonization process particularly in structural and content loss functions.
-
Creating and Understanding a cartoonization process to a specific style to cartoon rather than a collection of styles.
-
Observed a high color pallet and coarse surface with a transformer backbone (ViT) rather than a CNN backbone (VGG19). We also observed an improvement in the cartoonization process as the size of the dataset increases particularly the ViT backbone.
|

|
An Efficient Approach to Super-Resolution with Fine-Tuning Diffusion Models
-
Explored the potential of pre-trained diffusion model SR3, specifically fine-tuning and zero-shot approaches for the task of image super-resolution.
-
Demonstrated the generalization ability of fine-tuning process of SR3. The fine-tuning process is evaluated with limited time steps, iterations and data samples.
-
Evaluated the zero-shot approach of using range-null space decomposition for super-resolution using unconditional DDPM with using a conditional DDPM SR3 trained from scratch.
|

|
Optical Flow Less Video Frame Interpolation
-
Designed a lightweight video restoration transformer to capture long-range interactions, for fast inference and smaller training requirements for video frame interpolation. The model employs self-attention for feature extraction and mutual-attention as a surrogate to motion estimation to capture temporal information and feature alignment.
-
Created a training procedure to predict intermediate frames of the video which are continuous with subsequent frames by only looking at the previous frames essentially following causality.
-
Achieved comparable results with other SoTA video interpolation models.
|

|
Similarities between local-patch quality maps of NR IQA algorithms and saliency maps of computer vision classification models
-
Achieved an understanding of similarities between perception of images by humans and classification models. NR-IQA models trained on human judgments/quality ratings are used to replicate the perception of humans. Local-patch quality maps provide the key areas focused on while rating an image.
-
Using PaQ-2-PiQ to create local-patch quality maps for images. ResNet18 is trained on images rated as good-quality images by PaQ-2-PiQ and saliency maps are generated using Grad-CAM.
-
Compared the variation in local-patch quality maps and saliency maps due natural scene distortions like brightness, contrast, jpeg-compression, motion-blur, zoom-blur, etc.
|
|
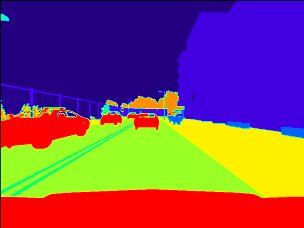
Reinforcement Learning for Autonomous Navigation of Cars
-
Applied reinforcement learning for autonomous navigation of cars with two objectives; the car stays in the lane and the speed of the car is under the speed limit. Understood the benefits and difficulties of using reinforcement learning techniques for autonomous navigation.
-
Designed the reward functions based on visual inputs from the camera using segmentation and lane detection models. The agent can regulate the speed and steering angle of the car and is trained using Deep-Q-Learning.
|
|
Effects of reduced frame corruptions on video classification
-
Used CNN-RNN architecture for classifying videos.
-
Designed various natural and adversarial single frame corruptions and understanding their impacts on classification.
-
Designed a reduced frame-level adversarial attack to fool the video classification model.
|







